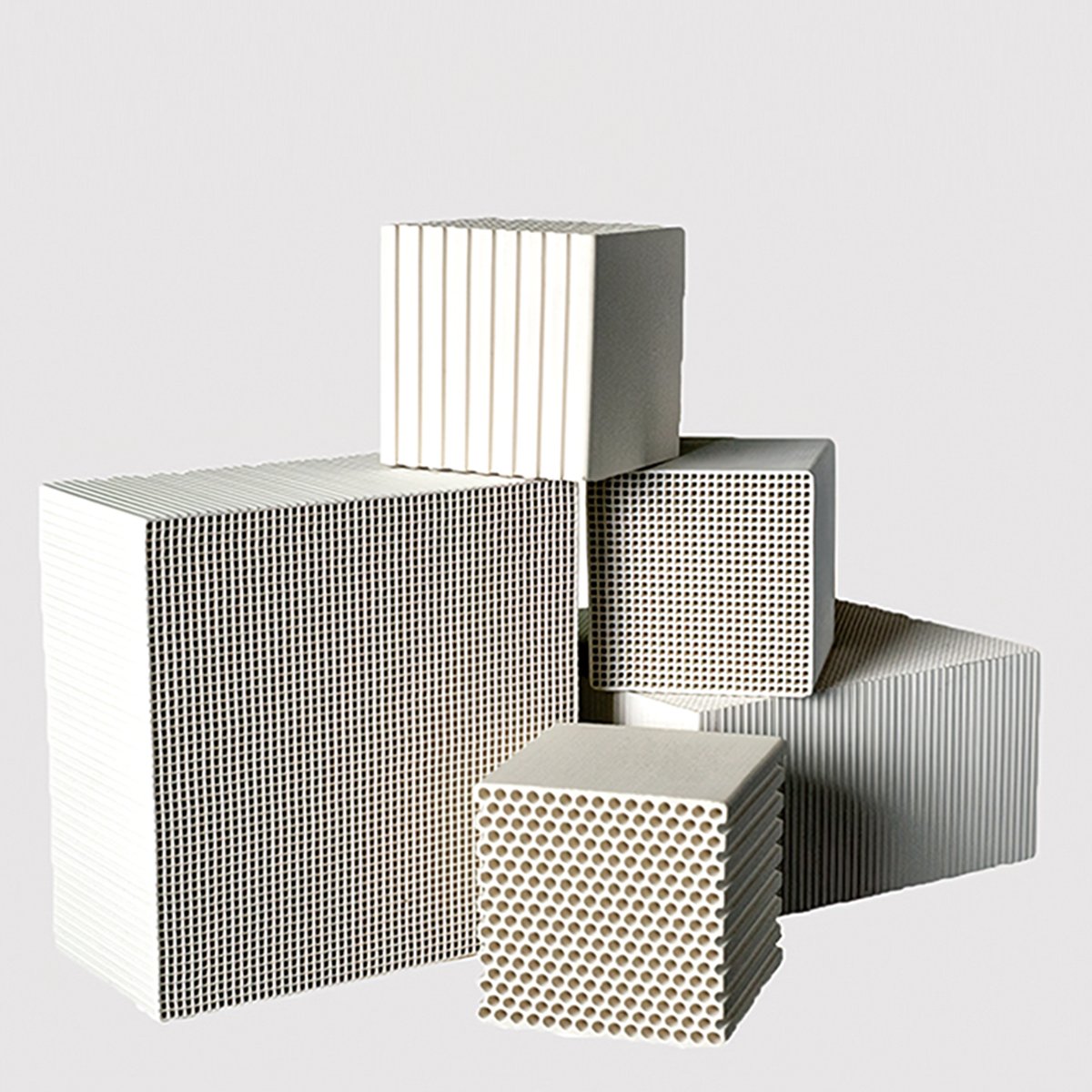
Ceramic Thermal Storage Materials
In the realm of ceramic thermal storage materials, cellulose and its derivatives can play pivotal roles in enhancing the performance and processing of these materials.
Advantages of incorporating cellulose into Ceramic Thermal Storage Materials
Binder in Ceramic Formulation
Cellulose, especially in the form of cellulose ethers, is used as a binder in the powder processing of ceramics. It aids in the formation of a uniform and cohesive green body before sintering (firing).
Adding cellulose improves the processability of the ceramic mix, ensuring it can be shaped effectively via extrusion, casting, or pressing. The organic material burns off during sintering, leaving behind a denser ceramic material. This results in improved mechanical strength and thermal storage capacity.
Pore-Forming Agent
Cellulose particles can be mixed with ceramic powders to act as a pore-forming agent. Upon heating, the cellulose combusts, leaving behind pores within the ceramic structure.
The introduction of porosity into ceramics can significantly enhance their thermal insulation properties. Pores within the material reduce thermal conductivity, making the ceramic more effective for thermal storage applications by slowing down heat transfer.
Rheology Modifier for Ceramic Slurries
In processes like tape casting, where thin ceramic layers are produced, cellulose derivatives are used to modify the rheology of the ceramic slurry.
Cellulose ethers can adjust the viscosity of the slurry, improving its flow properties and enabling the production of uniform, defect-free ceramic layers. This is crucial for producing ceramics with consistent thermal properties and structural integrity.
Improvement of Thermal Shock Resistance
Through the strategic introduction of cellulose-based fibers into ceramic matrices, manufacturers can enhance the thermal shock resistance of ceramics.
The fibers help to absorb thermal stresses during rapid temperature changes, preventing cracking and improving the durability of thermal storage ceramics. This is particularly beneficial in applications where the material is subjected to cyclic heating and cooling.
Enhanced Thermal Energy Storage
Cellulose derivatives can be incorporated into ceramic materials designed for phase change energy storage.
They can help to distribute the phase change materials (PCMs) evenly within the ceramic matrix, enhancing the thermal energy storage capacity of the material. This allows for more efficient storage and release of heat, which is advantageous in both heating and cooling applications.
In summary, the incorporation of cellulose into ceramic thermal storage materials offers significant advantages across various stages of production and in the final properties of the ceramics. From improved processing and mechanical strength to enhanced thermal performance and energy storage capabilities, cellulose contributes to advancements in ceramic technologies that are crucial for energy-efficient applications.
Related Products
Request an Instant Quote for Your Projects!
If you have specific questions about Ceramic Thermal Storage Materials
Our industry experts are here to help, and we’re happy to answer any questions you may have.