Finding trustworthy HPMC suppliers in China1 is challenging. Many buyers struggle with fake factories, quality inconsistencies, and communication issues that cost time and money.
To identify reliable HPMC manufacturers in China, verify their production capabilities through video calls, check business licenses, request factory audits, and visit facilities when possible. Always ask for product certifications and test samples before placing large orders.

In my 15 years running Wanhong's HPMC production, I've seen many distributors burned by unreliable suppliers. Let me share insider knowledge to help you avoid these costly mistakes and find genuine manufacturers.
How to Find Genuine Manufacturers in China?
The construction chemical market is flooded with trading companies posing as factories. Many buyers waste months dealing with middlemen who lack quality control and charge unnecessary markups.
Genuine HPMC manufacturers in China will have production facilities with multiple production lines, appropriate certifications (ISO 90012, SGS), technical support teams, and R&D capabilities3. They typically have minimum order quantities of 500-1000kg and offer customized solutions.

Key Indicators of Genuine HPMC Factories
Finding a real factory requires careful investigation. From my experience running our 6 production lines at Wanhong, I can tell you several reliable ways to distinguish genuine manufacturers from traders.
First, check their facility details. Authentic HPMC factories require substantial infrastructure—reactors, etherification equipment, drying systems, and grinding facilities. When contacting potential suppliers, ask specific technical questions about their production capacity, technology type (e.g., solvent method vs. water method), and annual output. Traders typically provide vague answers or need time to "check with the factory."
Second, evaluate their technical knowledge. Real manufacturers can discuss viscosity profiles, substitution degrees, particle size distribution, and application-specific modifications without hesitation. Last month, a customer asked me detailed questions about moisture content control during summer production—something only someone with hands-on manufacturing experience could answer thoroughly.
Finally, request certifications and test reports directly from certification bodies when possible. Legitimate factories maintain ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and often industry-specific certifications. Some even welcome third-party audits or factory inspections through services like SGS or Bureau Veritas.
| Indicator | Genuine Manufacturer | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Technical knowledge | Detailed, specific answers | Vague, delayed responses |
| MOQ | Usually 500-1000kg | Can offer smaller quantities |
| Price flexibility | Less negotiation room on small orders | Often more flexible |
| Sample customization | Can produce custom samples | Limited to available stock |
| Lead time | Consistent based on production schedule | Often varies significantly |
How to Verify a Supplier in China?
Many buyers have lost thousands of dollars to fraudulent companies with impressive websites but no actual factories. Verification requires multiple steps beyond basic online research.
To verify HPMC suppliers in China1, request their business license, check their registration through the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System, confirm their export license, and review their tax registration certificate. Video tours of production facilities provide additional verification.

Effective Supplier Verification Methods
Verifying suppliers thoroughly has saved our customers significant headaches. I recommend implementing a multi-layered verification approach beyond just checking a website or Alibaba profile.
Start with legal documentation verification. Every legitimate Chinese manufacturer must have a business license that you can verify through China's National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn). Check that the business scope specifically mentions cellulose ether or HPMC production. Trading companies will typically list "import/export" or "trading" activities instead. Pay attention to the registered capital—genuine HPMC factories require substantial investment, usually millions of RMB.
Next, conduct virtual verification through video calls. Request a live walkthrough of their production facility during operational hours. During these calls, ask to see specific equipment like reactors and packaging lines. Listen for background noise consistent with manufacturing operations. I recently conducted such a call with a potential partner from Saudi Arabia—seeing their reaction to our actual production scale built immediate trust.
Third-party verification provides additional security. Services like SGS, Bureau Veritas, and TÜV offer supplier verification audits. These professionals visit the facility, verify equipment, check production capabilities, and provide detailed reports. Though these services cost $500-1500, they're invaluable for first-time purchases or large orders.
| Verification Method | What to Look For | Red Flags |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Manufacturing in business scope, 5+ years history | Recently established, trading only |
| Video Tour | Equipment in operation, technical staff | Empty facilities, reluctance to show certain areas |
| Sample Testing | Consistent specifications, proper packaging | Variable quality between samples, generic packaging |
| References | Customers in your region/industry | Unable to provide references or only Chinese references |
| Payment Terms | Standard terms (30% deposit) | Demanding 100% advance payment |
How Many Grades of HPMC Are There?
Buyers often purchase the wrong HPMC grade because suppliers don't explain technical differences. This leads to product failures and wasted investment on inappropriate materials.
HPMC is available in approximately 8-12 primary grades based on viscosity (ranging from 5 to 200,000 mPa·s), methoxyl content (19-30%), hydroxypropoxyl content (4-12%), and particle size (fine to coarse). Each grade serves specific applications in construction, pharmaceuticals, or food industries.
Understanding HPMC Grade Classification
HPMC grade selection significantly impacts your final product performance. In my years producing HPMC for global customers, I've seen how grade mismatches cause serious application problems.
The primary classification of HPMC grades begins with viscosity, which ranges from very low (5-10 mPa·s) to ultra-high (100,000+ mPa·s). This property directly affects water retention, workability, and setting time in construction applications. For instance, tile adhesives typically require medium viscosity grades (15,000-30,000 mPa·s) to balance workability and sag resistance, while self-leveling compounds need lower viscosity grades (5,000-15,000 mPa·s) for proper flow characteristics.
Substitution type creates another classification layer, with methoxyl and hydroxypropoxyl content determining water solubility, thermal gelation, and surface activity. Construction-grade HPMC typically features methoxyl content of 19-24% and hydroxypropoxyl content of 7-12%, offering balanced water retention without excessive stickiness. Pharmaceutical grades often have higher methoxyl content for specific dissolution profiles.
Particle size distribution forms the third classification factor, with options including fine powder (95% passing through 100 mesh), surface-treated (for improved dissolution), and granular (for dust reduction). Each affects dissolution speed and handling properties. Most construction applications use surface-treated powders that resist lumping during mixing.
| Viscosity Level | mPa·s Range | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-low | 5-100 | Paint, coating additives |
| Low | 100-5,000 | Self-leveling compounds |
| Medium | 5,000-30,000 | Tile adhesives, renders |
| High | 30,000-75,000 | Plasters, EIFS systems |
| Ultra-high | 75,000-200,000 | Specialized formulations |
What is the Difference Between HPMC K and E Series?
Many buyers select the wrong HPMC series because they don't understand the fundamental differences between K and E types, leading to formulation problems and product performance issues.
The main difference between HPMC K and E series lies in their substitution patterns. K series has more uniform substitution with higher hydroxypropoxyl content, offering better water retention and workability for construction uses. E series features more clustered substitution, providing better strength and water resistance for pharmaceutical applications.
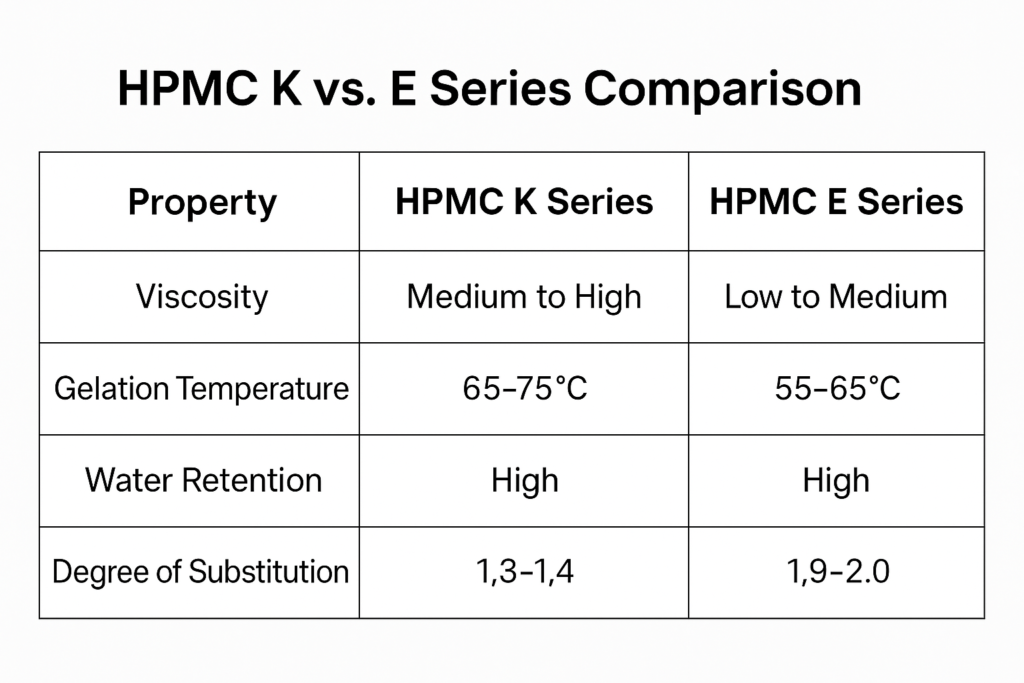
Critical Differences Between K and E Series HPMC
The choice between K and E series HPMC can dramatically affect your product performance. Through supplying both types to customers worldwide, I've observed how these differences impact real-world applications.
The fundamental difference lies in molecular structure and substitution pattern. K series HPMC (also known as Hypromellose 2208 in pharmaceutical terms) features more uniform distribution of methoxy and hydroxypropoxy groups along the cellulose backbone. This creates more consistent hydration and viscosity development. In contrast, E series (Hypromellose 2910) has more clustered substitution patterns, which affects its hydration properties and interaction with other ingredients.
Temperature response differs significantly between the series. K series typically exhibits thermal gelation at 65-70°C, while E series gels at higher temperatures (75-80°C). This property is crucial in applications where processing temperature varies. I recall a customer in the UAE who switched from E to K series in their exterior render and experienced significantly improved workability during hot weather application, as the K series maintained appropriate consistency despite the high ambient temperatures.
Water retention capabilities also vary meaningfully between the series. K series generally provides 15-20% better water retention than equivalent viscosity E series, making it preferred for cement-based applications where extended open time and thorough cement hydration are essential. E series, however, often provides better finished surface appearance in certain coating applications.
| Property | K Series | E Series |
|---|---|---|
| Methoxyl content | 19-24% | 28-30% |
| Hydroxypropoxyl content | 7-12% | 4-7.5% |
| Thermal gelation | 65-70°C | 75-80°C |
| Water retention | Excellent | Good |
| Common applications | Construction materials | Pharmaceuticals, food |
| Cost | Typically 5-15% higher | Standard pricing |
| Global availability | Widely available | More common in pharma markets |
Conclusion
Finding reliable HPMC manufacturers requires verifying production capabilities, understanding product grades, and knowing the differences between series types. With these insights, you can confidently source high-quality HPMC for your projects and avoid costly supplier mistakes.