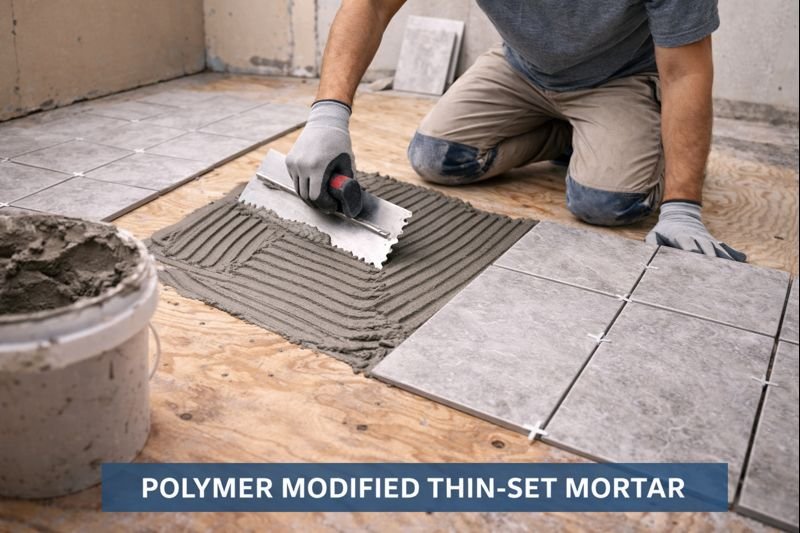
Confused by all the different HPMC grades on the market? You're not alone. Many construction material buyers struggle to choose the right hydroxypropyl methylcellulose1 for their specific applications, leading to costly mistakes.
HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose) grades are classified based on viscosity, molecular weight, and substitution degree. The perfect grade depends on your specific application - construction adhesives need high viscosity (100,000+ mPa·s), while pharmaceutical applications require specific substitution patterns and lower viscosity ranges (3-15 mPa·s).
Finding the right HPMC grade is crucial for your product's success. Just last month, I helped a client who had been using the wrong viscosity grade in their tile adhesive. After switching to our recommended grade, their product's performance improved dramatically and complaints dropped by 40%. Let me guide you through everything you need to know about HPMC grades.
What is HPMC and Why is it So Versatile?
If you've worked with construction materials, pharmaceuticals, or food products, you've likely encountered HPMC without realizing it. Its varying properties can be overwhelming when trying to select the right type.
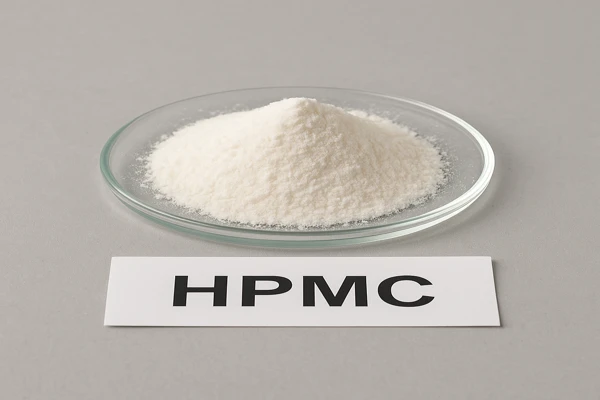
HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose2) is a semi-synthetic, non-ionic cellulose ether derived from natural cellulose. It features both methoxy (-OCH3) and hydroxypropyl (-OCH2CH(OH)CH3) substitution groups, creating a versatile polymer that's water-soluble and forms temperature-dependent gels with unique properties.
HPMC has become indispensable in numerous industries due to its remarkable versatility. The key to this versatility lies in its customizable nature through controlled manufacturing processes. During production, we can precisely adjust parameters like viscosity, particle size, substitution degree, and molecular weight to create specific grades for different applications.
In our factory, we produce HPMC with viscosities ranging from as low as 3 mPa·s to as high as 200,000 mPa·s. The substitution degree (which determines properties like water retention and gel temperature) can also be tailored to specific needs. For construction applications, we typically aim for methoxyl content between 19-24% and hydroxypropyl content between 7-12%, while pharmaceutical grades might require different substitution patterns.
HPMC Viscosity Grades and Their Applications
| Viscosity Range (mPa·s) | Common Grade Designations | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 3-15 | K3, K5, K15 | Pharmaceutical coatings, ophthalmic solutions |
| 15-100 | K30, K50, K100 | Tile adhesives, paint thickeners, joint compounds |
| 100-4,000 | K250, K400, K4M | Cement-based mortars, self-leveling compounds |
| 4,000-15,000 | K4M, K15M | High-strength adhesives, plasters |
| 15,000-100,000+ | K30M, K100M | Specialty construction products, high water retention applications |
HPMC Grades Classification: How Do They Differ?
When faced with product codes like "HPMC K15M" or "HPMC E5," many buyers get confused about what these designations actually mean. Making the wrong choice can lead to product failures.
HPMC grades are classified using a standardized system based on viscosity and substitution type. The letter (K, E, F) indicates the substitution pattern, while the number represents viscosity. For example, K4M indicates a K-type HPMC with 4,000 mPa·s viscosity, while E5 indicates an E-type with 5 mPa·s viscosity.

The classification of HPMC grades3 is more complex than it initially appears. Let's break down the key parameters that differentiate various HPMC grades:
- Substitution Type: The letters K, E, F, and others refer to different patterns of methoxyl and hydroxypropyl substitution on the cellulose backbone.
- K-type: Contains 19-24% methoxyl and 7-12% hydroxypropyl groups. This is our most popular type for construction applications due to its excellent water retention.
- E-type: Contains 28-30% methoxyl and 7-12% hydroxypropyl groups. This type forms gels at higher temperatures (65-70°C) compared to K-type.
- F-type: Contains 27-30% methoxyl and 4-7.5% hydroxypropyl groups. These have specialized applications in pharmaceuticals.
- Viscosity: The number in the grade designation indicates the approximate viscosity in mPa·s (or cP) measured in a 2% aqueous solution at 20°C.
- For example, K100M indicates a viscosity of approximately 100,000 mPa·s.
- The suffixes often indicate magnitude: M = 1,000 (from "mille"), C = 100 (from "centum").
- Particle Size: Though not always included in the grade designation, particle size significantly affects dissolution rate.
- Our standard grades typically range from 80-100 mesh.
- Fine powder grades (designated with "F") are available for applications requiring rapid dissolution.
- Coarse grades might be used when slower dissolution is preferred.
At our factory, we've developed specialized grades beyond the standard classifications to meet specific customer requirements, such as adjusted gel temperatures, enhanced water retention, or modified dissolution profiles.
Selection of HPMC Grades: How to Choose the Right One?
I've seen many clients struggle with product failures simply because they selected an inappropriate HPMC grade. Understanding your application requirements is the first step toward making the right choice.
The right HPMC grade selection depends on your specific application requirements. For construction adhesives, grades like K15M or K100M provide excellent water retention and workability. For pharmaceutical tablets, lower viscosity grades like E5 or K100 offer better binding properties.
Selecting the perfect HPMC grade4 requires a systematic approach that considers multiple factors. In my 15+ years working with HPMC, I've developed a reliable method to help clients choose the optimal grade for their applications. Here's my process:
First, identify your primary performance requirements. Are you looking for water retention, thickening, binding, film formation, or a combination of these properties? For example, in tile adhesives, water retention is critical to prevent premature drying and ensure proper cement hydration. For this application, K-type HPMC with viscosities between 15,000-100,000 mPa·s typically works best.
Next, consider your processing conditions. If you're using high-shear mixing equipment, you might prefer a coarser particle size to prevent dusting and allow for controlled dissolution. For applications requiring rapid dissolution, our fine-grade options provide almost immediate functionality.
Don't overlook environmental factors. Will your product be used in extreme temperatures? For hot climate applications like in Saudi Arabia or UAE, we recommend grades with higher gel temperatures to maintain stability. Our specially formulated "HT" grades maintain their properties even at temperatures above 40°C.
Budget constraints are also important. Higher viscosity grades typically cost more per kilogram, but you often need less of them to achieve the desired effect. We can help you optimize the cost-performance ratio by suggesting alternatives or custom blends that meet your requirements while keeping costs manageable.
HPMC Grade Selection Guide for Common Applications
| Application | Recommended HPMC Grades | Key Properties Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Tile Adhesives | K15M, K30M | High water retention, extended open time |
| Self-leveling Compounds | K4M, K15M | Moderate viscosity, good flowability |
| Cement Renders | K100, K400 | Good workability, moderate water retention |
| Joint Compounds | K15, K30 | Low-medium viscosity, good sag resistance |
| Wall Putties | K15, K30, K100 | Varies by formulation, typically low-medium viscosity |
| Exterior Insulation Systems | K15M, K30M | High water retention, good adhesion |
Is HPMC Safe for Humans?
With increasing focus on product safety, many of my clients want to know if HPMC poses any health risks to workers or end-users. These concerns are valid and deserve a clear answer.
HPMC is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by global regulatory bodies including the FDA and EFSA. It has extremely low toxicity with an LD50 >10,000 mg/kg body weight, making it safer than table salt. It's non-irritating to skin and eyes in typical concentrations.

The safety profile of HPMC5 is one of its most significant advantages across various applications. As a factory owner producing over 15,000 tons of HPMC annually, I can confidently address safety concerns based on extensive testing and decades of industry experience.
HPMC has undergone rigorous toxicological evaluations worldwide. The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) has assigned it an "ADI not specified" status, which is their highest safety classification, indicating no limits on daily intake are necessary. This makes it suitable for direct food contact and pharmaceutical applications.
For construction workers handling HPMC-containing products, the safety considerations are minimal. The primary concern is dust exposure during mixing of dry powders. We recommend basic dust masks when handling large quantities of dry HPMC powder. Once in solution or incorporated into formulations, HPMC poses negligible respiratory risks.
Environmental safety is also excellent. HPMC is biodegradable, breaking down into cellulose, water, and carbon dioxide. It doesn't bioaccumulate in organisms or persist in ecological systems. Our wastewater from HPMC production undergoes treatment to ensure environmental compliance, and we've implemented closed-loop systems to minimize waste.
All our HPMC grades undergo regular testing for heavy metals, residual solvents, and microbial contamination to ensure they meet or exceed international safety standards. We provide complete safety data sheets for all our products, detailing handling procedures, exposure limits, and emergency measures.
What is HPMC Used For?
Many new clients come to me with only a vague understanding of HPMC's applications. They're often surprised to learn about its widespread use across multiple industries beyond their own.
HPMC is widely used across construction (as a water-retention agent in mortars, thickener in paints), pharmaceuticals (tablet coatings, controlled release matrices), food industry (stabilizer, thickener), personal care products (gelling agent), and even in oil drilling (fluid loss control).
The versatility of HPMC across industries is truly remarkable. Let me walk you through the major application areas and the specific functions HPMC performs in each:
In construction, which accounts for approximately 70% of global HPMC consumption, it serves multiple crucial functions. In dry-mix mortars, HPMC primarily provides water retention, preventing premature water loss to porous substrates like concrete or brick. This ensures proper cement hydration and stronger bonds. It also improves workability, sag resistance, and open time for tile adhesives.
In our testing laboratory, we've demonstrated that properly selected HPMC grades can extend the open time of tile adhesives by up to 30 minutes even in hot, dry conditions.
The pharmaceutical industry relies on specific pharmaceutical-grade HPMC6 for tablet manufacturing. HPMC forms hydrophilic matrix systems that control drug release rates, with different viscosity grades providing release periods ranging from 4 to 24 hours. It's also used in tablet coating, where it forms films that protect active ingredients from moisture and oxygen while masking bitter tastes.
Our pharmaceutical-grade HPMC undergoes additional purification steps to meet USP/EP/JP standards.
In the food industry, HPMC functions as a thickener, stabilizer, and emulsifier. It prevents ice crystal formation in frozen foods, stabilizes foams in whipped products, and improves texture in gluten-free baking. The unique thermal gelation properties of HPMC are particularly valuable in fried foods, where it forms a barrier that reduces oil absorption by up to 40%.
Less known applications include its use in ceramic processing (as a binder and plasticizer), 3D printing (as a temporary support material), and in agriculture (as a seed coating and soil conditioner). We've even supplied HPMC for specialized applications in archaeological conservation for stabilizing ancient artifacts.
What are the Side Effects of HPMC?
When discussing HPMC with potential clients, safety questions inevitably arise. Understanding potential side effects is important for responsible use and addressing end-user concerns.
HPMC has minimal side effects. In very high concentrations, it may cause mild gastrointestinal discomfort if ingested. For construction applications, dust inhalation during mixing is the primary concern, easily mitigated with basic dust masks. Skin contact is non-irritating for most people.

While HPMC is recognized as one of the safest industrial chemicals in use today, it's important to understand its potential side effects, however minor they may be. This knowledge helps ensure appropriate handling and addresses concerns that may arise from end-users or regulatory inquiries.
For construction applications, the primary exposure route is through dust inhalation during the mixing of dry-mix products. Our studies show that HPMC dust is considered a "nuisance dust" rather than a hazardous substance.
It may cause temporary respiratory irritation in sensitive individuals if inhaled in large quantities, but it doesn't cause permanent lung damage. Standard dust masks (N95 or equivalent) provide adequate protection for workers.
In pharmaceutical applications, where HPMC is ingested, side effects are rare even at relatively high doses. Occasional reports include mild bloating, gas, or laxative effects when consumed in large quantities (several grams at once). These effects are temporary and resolve without intervention. In controlled clinical studies, doses exceeding 10 grams per day showed no significant adverse effects in most participants.
For those with specific sensitivities, very rare allergic reactions to HPMC have been documented in medical literature, primarily in the context of eye drops containing HPMC as a lubricant. These reactions typically manifest as eye redness and irritation and resolve when use is discontinued.
From an environmental perspective, HPMC presents minimal concerns. Its biodegradability means it doesn't persist in ecosystems. However, like any organic material, very large quantities released into waterways could temporarily increase biological oxygen demand. Our production facility employs wastewater treatment processes that effectively remove HPMC before discharge.
One practical consideration worth noting is that HPMC solutions can be extremely slippery when spilled on floors, potentially creating fall hazards. We recommend immediate cleanup of any spills using absorbent materials followed by thorough rinsing.
Is HPMC7 Vegan?
In recent years, I've noticed increasing inquiries about the vegan status of our products. This reflects growing consumer awareness across all industries, including construction materials.
Yes, HPMC is 100% vegan. It's derived from plant cellulose (typically wood pulp or cotton linters) through chemical modification. No animal products or by-products are used in its production. It's suitable for vegan-friendly products in food, pharmaceuticals, and construction applications.

The vegan status of raw materials has become increasingly important across all industries, not just in food and personal care products. As someone directly involved in HPMC manufacturing, I can provide definitive information on this topic.
HPMC production begins with refined cellulose derived exclusively from plant sources. In our facility, we primarily use cellulose from sustainably managed forests, specifically hardwood sources that provide the optimal cellulose structure for our processes.
The cellulose undergoes alkalization with sodium hydroxide, followed by treatment with propylene oxide and methyl chloride to introduce the hydroxypropyl and methyl groups that give HPMC its unique properties.
Throughout this entire manufacturing process, no animal-derived materials or processing aids are used. All catalysts, solvents, and processing chemicals are either synthetic or plant-derived. We've conducted a thorough analysis of our supply chain to verify
The Ultimate HPMC Grades Breakdown: Finding the Perfect Fit for Your Needs?Throughout this entire manufacturing process, no animal-derived materials or processing aids are used. All catalysts, solvents, and processing chemicals are either synthetic or plant-derived. We've conducted a thorough analysis of our supply chain to verify that no animal-derived materials are introduced at any stage.
This vegan status makes HPMC particularly valuable for manufacturers seeking to create fully plant-based products. In the construction industry, this might not seem immediately relevant, but the trend toward "cruelty-free" building materials is growing, particularly in eco-conscious markets. Some certification programs for sustainable buildings now include criteria related to animal-derived components.
For food applications, HPMC's vegan nature makes it an excellent stabilizer and thickener for plant-based foods. It's commonly used in vegan ice creams, plant-based meat alternatives, and gluten-free baked goods as a replacement for animal-derived ingredients like gelatin or eggs.
In pharmaceuticals, HPMC provides an alternative to gelatin for capsule shells and coatings. The global market for vegetarian capsules (primarily HPMC-based) is growing at over 10% annually, driven largely by consumer demand for vegan-friendly medications and supplements.
It's worth noting that while HPMC itself is vegan, finished products containing HPMC may contain other non-vegan ingredients. For manufacturers creating vegan-certified products, we provide documentation confirming the plant-based origin of our HPMC to support their certification processes.
Conclusion
Choosing the right HPMC grade is crucial for your product's success. Consider your application's specific requirements for viscosity, substitution type, and particle size. Our grades are safe, vegan, and versatile across multiple industries, and we're always available to help you find your perfect match.
-
Explore this link to understand the diverse applications of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in construction, ensuring you choose the right grade for your needs. ↩
-
Explore the diverse applications of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose to understand its significance in construction, pharmaceuticals, and food products. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the various HPMC grades and their specific applications, ensuring you choose the right one for your needs. ↩
-
Explore this resource to understand the systematic approach to selecting the right HPMC grade for various applications. ↩
-
Understanding the safety profile of HPMC is crucial for industries using it. Explore this link to learn more about its safety evaluations and classifications. ↩
-
Learn about the critical role of pharmaceutical-grade HPMC in controlling drug release and enhancing tablet quality. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the versatile applications of HPMC in various industries and its safety profile. ↩